This post contains affiliate links.
Eleven common questions about the migration of Arkansas hummingbirds are discussed in this article.
There Are Eleven Hummingbirds Documented As Arkansas Hummingbirds.
Listed In The Order Of Frequency Seen:
| Hummingbirds: | Number seen: | Documented: | % seen: |
| Ruby-throated | 34,963 | Documented | 87.85% |
| Rufous | 3,552 | Documented | 8.92% |
| Black-chinned | 413 | Documented | 1.04% |
| Calliope | 305 | Documented | 0.77% |
| Broad-billed | 180 | Documented | 0.45% |
| Buff-bellied | 123 | Documented | 0.31% |
| Anna’s | 116 | Documented | 0.29% |
| Broad-tailed | 77 | Documented | 0.19% |
| Mexican Violetear | 69 | Documented | 0.17% |
| Allen’s | 1 | Documented | 0.00% |
| Rivoli’s | 1 | Documented | 0.00% |
| Total seen: | 39,800 |
Click “Documented” link above to see current eBird sighting statistics for Arkansas.
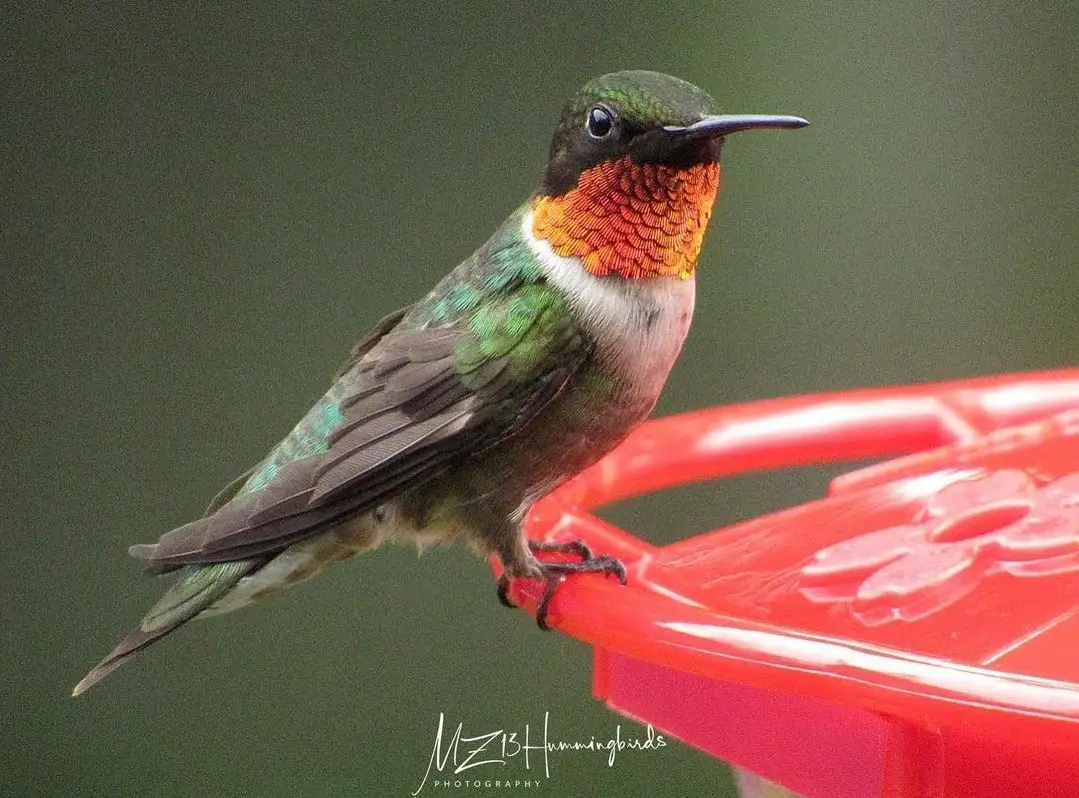

Photo by: mz13hummingbirds
When do Arkansas hummingbirds arrive?
The earliest arrivals of Arkansas hummingbirds are seen in late March, and new arrivals continue through June.
Arkansas hummingbirds begin their spring migration north from as far away as Panama or as close as Mexico. Arkansas hummingbirds arrive in Arkansas as early as March, while some late migrators may arrive as late as June. but by the end of June, all hummingbirds that are migrating further than Arkansas are gone from Arkansas.
The first migrating hummingbirds will be males, followed by females about a week later. The males arrive first to stake out the territory that they will defend as they try to attract a female.
Ruby-throated hummingbirds are by far the most commonly seen Arkansas hummingbirds and will be the first migrating hummingbirds to be seen in Arkansas. Rufous hummingbirds are a distant second most common hummingbirds seen in Arkansas.
Watch for the male’s vividly colored gorget; a week or so later, the females will begin to appear at your feeders.
See my article: How to Identify a Hummingbird’s Gender in 4 Easy Steps
According to the Missouri Department Of Conservation, if Arkansas hummingbird enthusiasts start feeding them when they arrive, there is less chance they will move on and will decide to spend the summer in Arkansas.
Arkansas hummingbirds starting their spring migration north from Panama City, Panama need to fly about 3,357 miles to reach Little Rock, Arkansas if they fly over land the entire way. Those choosing to fly over the Gulf of Mexico will need to fly 1,949 miles.
Arkansas hummingbirds starting their journey north from Mexico, at the United States’ southernmost border at Brownsville Texas, need to fly 684 miles to reach Little Rock, Arkansas.
Are there Arkansas hummingbirds that live in the state year-round?
There are no hummingbird species that live in Arkansas year-round, however, the Rufous, Anna’s, and Black-chinned hummingbirds are documented as seen in the middle of winter.
The Ruby-throated hummingbird lives in Arkansas year-round.
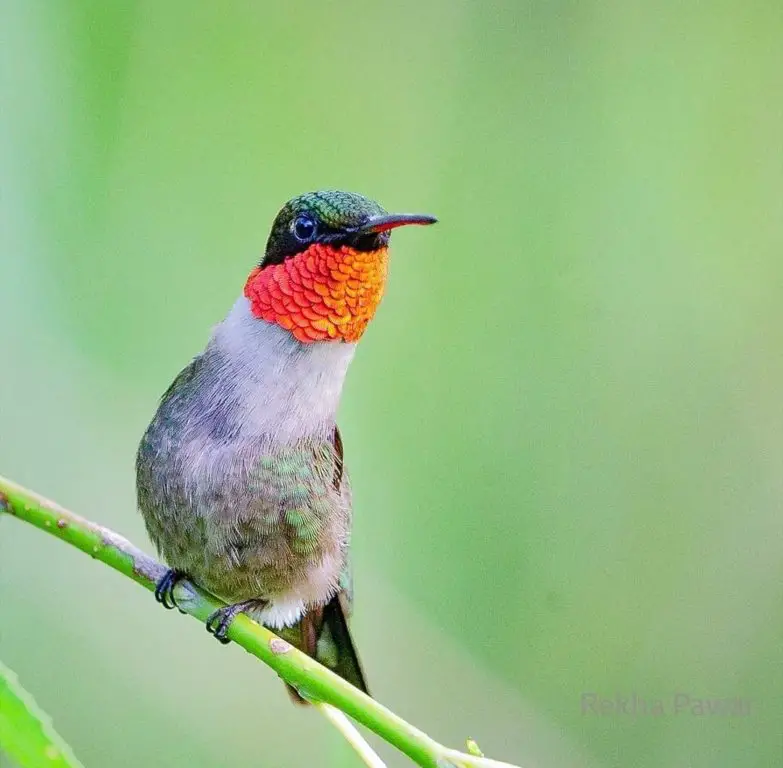

Photo by: Rekha Pawar
Hummingbirds seen in Arkansas during the winter:
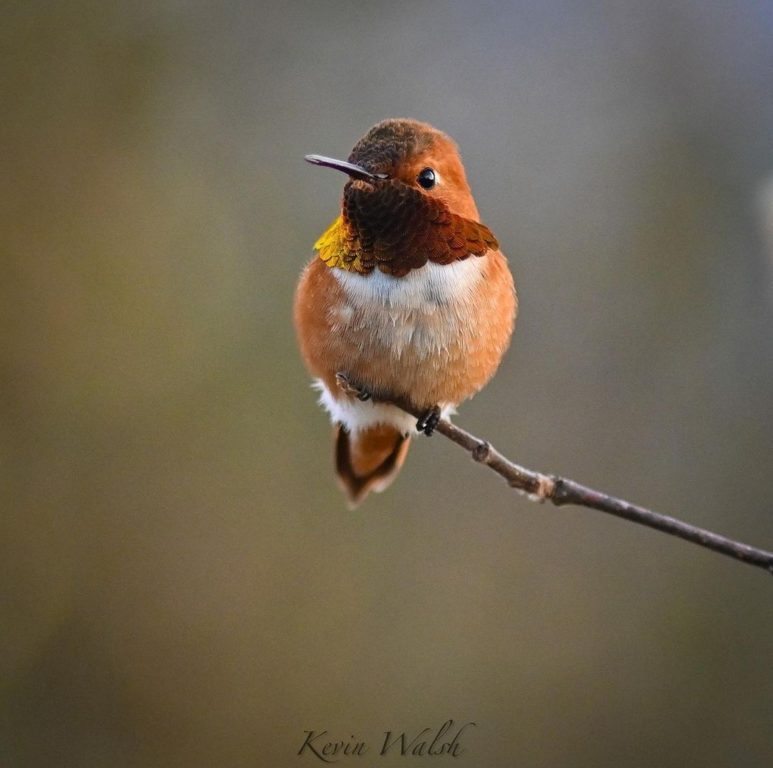

Photo by: Kevin Walsh
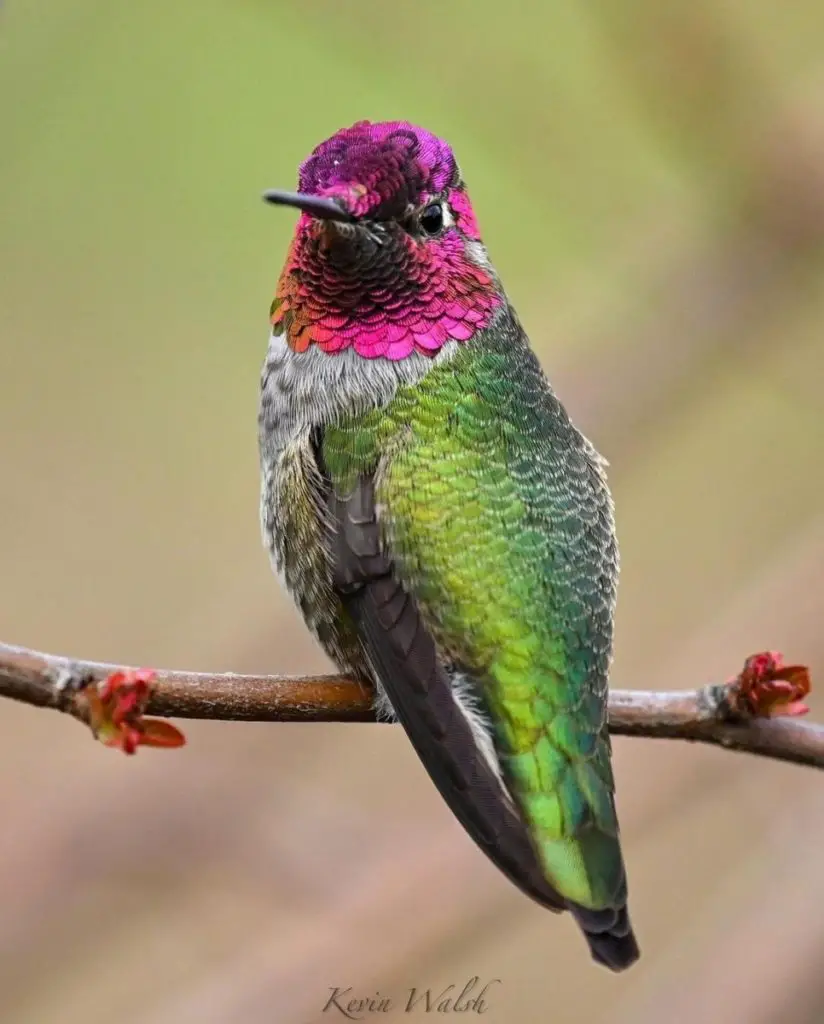

Photo by: Kevin Walsh

Photo by: hummingbirdsbysuprise
The general public is unaware of how cold-tolerant hummingbirds actually are.
Some banded hummingbirds have been observed at temperatures as low as -9 degrees Fahrenheit with a wind chill of -36 degrees Fahrenheit, according to eBird.org.
Which Arkansas hummingbirds breed and nest in the state?
The Ruby-throated and Anna’s hummingbirds are the only hummingbirds that breed and nest in Arkansas.

Photo by: paulapaintsart

Photo by: Kevin Walsh
Ruby-throated – The Ruby-throated hummingbird has an extensive breeding area that covers the entire eastern half of the United States and extends into Canada as far west as Alberta.
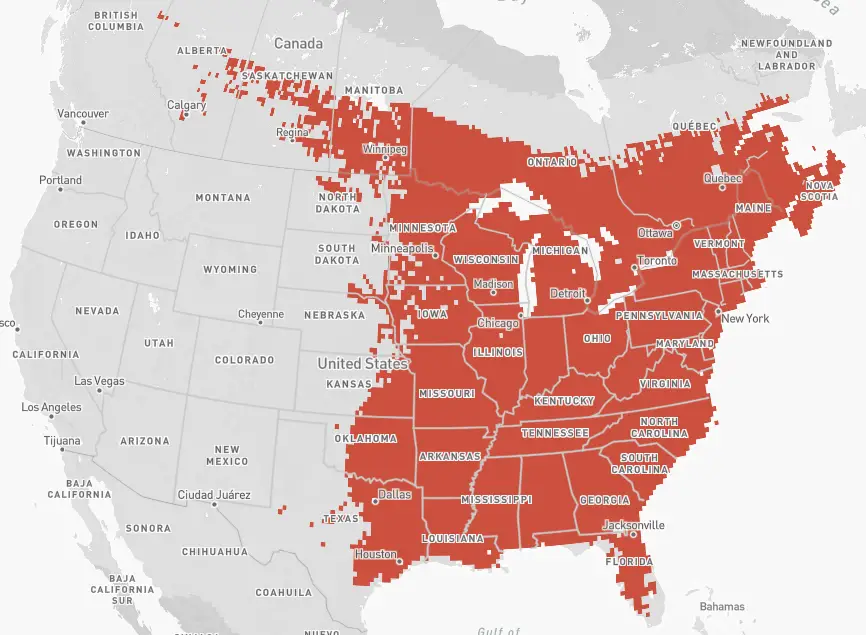
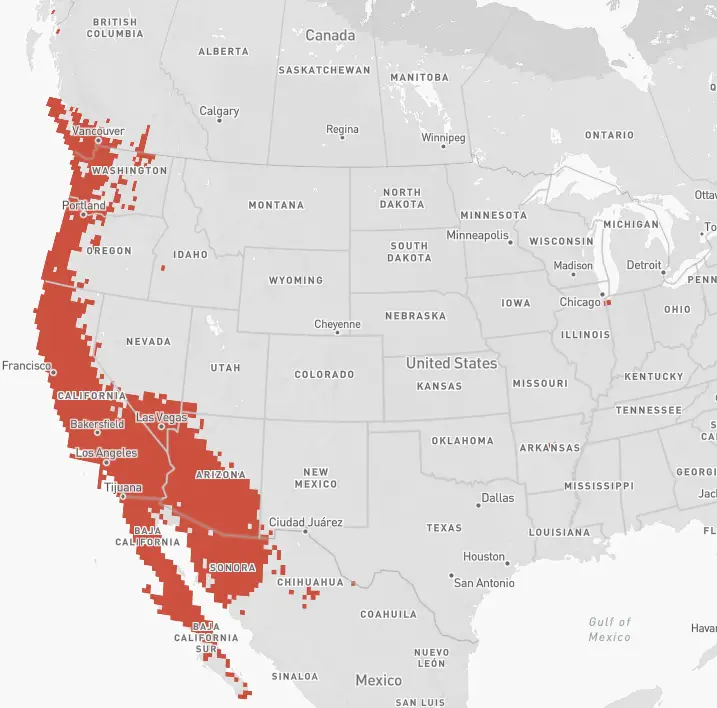
Anna’s – The Anna’s hummingbird breeds primarily along the western coastline of North America from Vancouver, BC to the southernmost tip of Baja California and extending eastward in central California to include the southern tip of Nevada, about 75% of Arizona, and into the western coast of upper Mexico.
There are isolated scattered breeding areas identified in Idaho, Arkansas, the Chicago area, and northern British Columbia.
The entire reason for northern migration, much like salmon swimming upstream to their place of birth to lay eggs, is for female hummingbirds to return to the area where they were born to build a nest, mate, and raise a family.
When a female hummingbird arrives at the breeding grounds, her attention shifts to building a nest and then looking for a mate.
Hummingbird females prefer to build their nests in deciduous trees, 10 to 20 feet above the ground.
It will take her between 5 and 7 days to construct the nest of materials such as plant down, moss, and fine plant fibers, decorated with lichens and held together by spider webs.
See my article: Hummingbird Parents: (Mating to Nesting)
See my article: Baby Hummingbirds: (Egg to Fledgling)
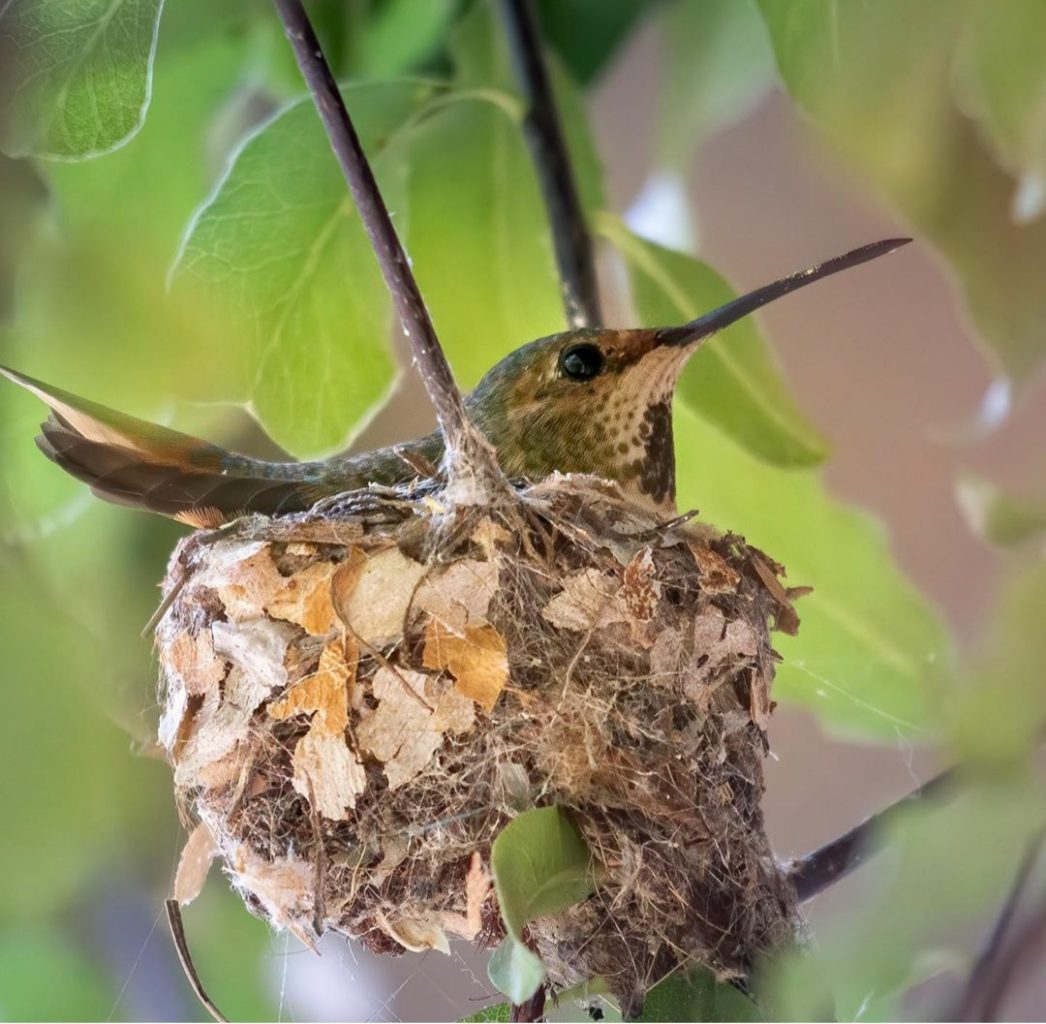

Photo by: Aaron Gomperts
Each species of male hummingbird has its own unique mating dance ritual of courtship to attract a female. They do perfectly choreographed dives and dance maneuvers to attract a flirty female.
See my article: Hummingbird Dance: 5 Interpretive Explanations
During the mating ritual, there is no penetration since male hummingbirds lack external sexual organs.
The “Cloacal Kiss occurs when the cloacae, (pronounced “kloh-ay-see”), of both hummingbirds are brought together during the brief mating procedure, which lasts only three to five seconds.
After the Cloacal kiss, the female must begin building the nest immediately.
Each brood of hummingbirds typically produces two eggs, laid on consecutive days.
The majority of hummingbirds have two broods annually, although some may have more depending on the timing of their migration and the duration of the days they spend in their breeding areas.
Arkansas nesting hummingbirds usually have 2 broods per year but some may have time to work in a third brood.
When Should I Put Up My Feeders for Arkansas Hummingbirds?
Arkansas hummingbird enthusiasts should put out hummingbird feeders in March to attract the very earliest arriving migrating hummingbirds.
The majority of Arkansas migrating hummingbirds will arrive in May.
Hummingbird aficionados can reduce the likelihood that hummingbirds will leave the state and elect to spend the summer thereby providing food for them as soon as they arrive, according to the Missouri Department of Conservation.
Approximately one week after the arrival of the male hummingbirds, the females will follow.
Migrating hummingbirds will continue to arrive until about mid-June.
Hummingbirds seen in Arkansas after mid-June will be hummingbirds that will spend their entire summer in Arkansas.
Make sure to use high-quality nectar solutions in your hummingbird feeders; homemade nectar works best.
See my article: Forget Commercial Hummingbird Food, Try Making Homemade Nectar
See my article: The One Thing You Need to Eliminate From a Hummingbird’s Diet
How long do Arkansas hummingbirds stay in the state?
Arkansas hummingbirds stay in the state for at least six months.
They will start arriving as early as mid-March and most will be gone in October.
Some Rufous, Anna’s and Black-chinned, are seen in Arkansas during the winter, but most migrate south for the winter.
The general public is unaware of how tolerant hummingbirds actually are.
Some banded hummingbirds have been observed at temperatures as low as -9 degrees Fahrenheit with a wind chill of -36 degrees Fahrenheit, according to eBird.org.
Some migrating seasonal hummingbirds choose to over-winter in Arkansas and those too old or injured to migrate will be the only hummingbirds Arkansas hummingbird enthusiasts will see during the winter.
The extremely cold-tolerant Rufous, Anna’s and Black-chinned hummingbirds are the most probable migratory hummingbirds to decide to spend the winter in Arkansas.
In Pennsylvania, a state known for its cold harsh winters, the Valley Forge Audubon Society reports winter sightings of the Allen’s, Calliope, Rufous, and Black-chinned hummingbirds.
Because hummingbirds have such long memories, they will revisit the flowers and feeders they frequented during their spring migration and will remember them when they migrate back to the south in the fall.
See my article: Hummingbird Adaptation and Remarkable Ability to Locate Food
The most common Arkansas hummingbird seen during the hot summer months will be the Ruby-throated hummingbird.
In a distant second place will be the Rufous hummingbird.
Finding strategies to provide your hummingbirds with cool nectar might be crucial when the summer heat becomes unpleasant and tough to handle.
See my article: How to Help Hummingbirds in Hot Weather
When do Arkansas hummingbirds leave the state?
Arkansas hummingbirds begin leaving the state as early as August, and by late October they have migrated to their over-wintering areas in Mexico and Central America.
Most of Arkansas’s migrating hummingbirds are gone by the end of October but a few stragglers might stay until the end of the year.
A few older hummingbirds will be the first to start the fall migration, maybe as early as late August, depending on their strength and energy, with the youngest hummingbirds finishing the fall migration by mid-November.
The oldest hummingbirds will be the first to start migration according to an article from the University of Southern Mississippi.
This elongated migration time frame ensures late straggling migrants have enough food available to fuel their bodies before making the long taxing migration south for the winter.
Some migrating hummingbirds Arkansas will see during the winter are migrating hummingbirds that are too old or injured to migrate.
Hummingbird migration is triggered by the circadian (internal daily clock) and the circannual (yearly internal clock) rhythm.
Changes in the weather, temperature, time of the season, the decline in the food supply, and decreased amount of sunlight because of shortening days are all factors that trigger an individual hummingbird’s instinct to migrate.
As with spring migration, male hummingbirds are the first to begin the southern migration in the fall. The female migrating hummingbirds begin their southern fall migration as soon as they have completed raising their offspring and are able to migrate themselves.
When should I take down my feeders for Arkansas hummingbirds?
Mid-to-late October, or after a few weeks without any hummingbird sightings, is the ideal time to remove Arkansas hummingbird feeders for the winter.
Feeders are left up all winter by some Arkansasans to feed the uncommon winter hummingbirds and those that are too old or injured to migrate.
The dilemma hummingbird enthusiasts struggle with every year is whether to leave the hummingbird feeders up all year or take them down during the winter.
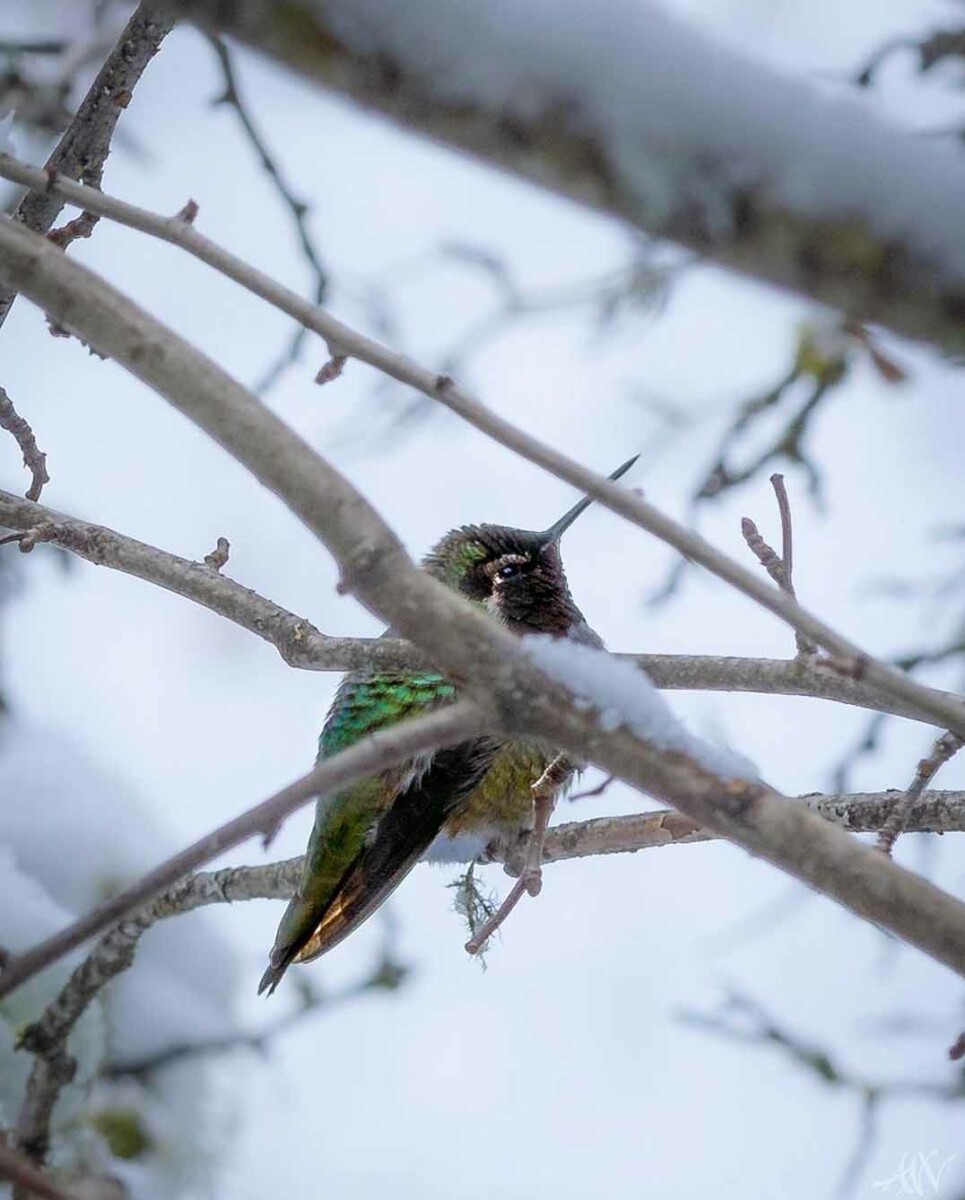

Male Anna’s hummingbird
The challenge then becomes preventing the nectar from hummingbirds from freezing.
See my article: 11 DIY Ways To Keep Hummingbird Nectar From Freezing
Investing in a hummingbird feeder warmer, like the Hummer Health feeder heater, is one approach to prevent hummingbird nectar from freezing.
Unfortunately, it is only compatible with a select few types of hummingbird feeders, like the Aspect’s HummZinger feeder.
The Ruby-throated, Rufous, Anna’s, and Black-chinned hummingbirds, who are Arkansas’ most likely uncommon winter visitors, depend on the nectar that some hummingbird fans leave out all winter long.
Most Allen’s, Anna’s, Black-chinned, Broad-billed, Broad-tailed, Buff-bellied, Calliope, Mexican violetear, Rivoli’s and Rufous hummingbirds will not spend the winter in Arkansas and will decide to migrate south to Mexico for the winter.
Ruby-throated hummingbirds will stay in Arkansas year-round.
Keeping hummingbird feeders up during the winter is a noble gesture that helps other migrating species that are injured or too old to migrate by providing them with nectar.
See my article: 11 DIY Ways to Keep Hummingbird Nectar From Freezing
See my article: Should I Keep My Hummingbird Feeder Out During the Winter?
Hummingbird enthusiasts who leave hummingbird feeders up all winter provide much-welcomed nutrition for late migrators and hummingbirds too old or injured to migrate.
The general public is unaware of how tolerant hummingbirds actually are.
Some banded hummingbirds have been observed at temperatures as low as -9 degrees Fahrenheit with a wind chill of -36 degrees Fahrenheit, according to eBird.org.
See my article: 3 Reasons Why Hummingbirds Are Banded
Hummingbirds that depend on these wintertime feeders may die if hummingbird feeders are taken down in the middle of winter during periods of below-freezing temperatures.
See my article: 11 DIY Ways to Keep Hummingbird Nectar From Freezing
How long does it take an Arkansas hummingbird to migrate?
An Arkansas hummingbird requires 23 hours of flying at its average flight speed of 30mph to fly from Little Rock, Arkansas, to the most distant USA/Mexican border, 684 miles away.
Hummingbirds migrating to Panama, 1,949 miles across the Gulf of Mexico or 3,357 over land, will need to fly 65 or 112 hours, respectively.
Some fly at a relaxed distance as slow as 1 hour per day, others fly up to 500 miles non-stop in about 20 hours as some do while migrating across the Gulf of Mexico.
Unlike other migrating birds, hummingbirds do not travel in flocks.
Individual hummingbirds travel according to their own internal clock.
This staggered migration pattern ensures resources are not consumed and depleted all at one time.
Hummingbirds regularly acquire between 25% and 50% of their body weight as migration draws nearby eating more nectar from feeders and blooming plants and by collecting more insects in midair for protein.
This rise in body fat provides the hummingbird with energy for its protracted migration flight.
Expect to see an increased volume of southern-migrating hummingbird visitors to your feeders in Arkansas during this fall migration from September through October.
The hummingbirds that visited your feeders during the spring migration will remember exactly where your feeder is located and will most likely revisit that same feeder on their way to their over-wintering area in Mexico and Central America.
See my article: Hummingbird Adaptation and Remarkable Ability to Locate Food
Where do Arkansas hummingbirds go in the winter?
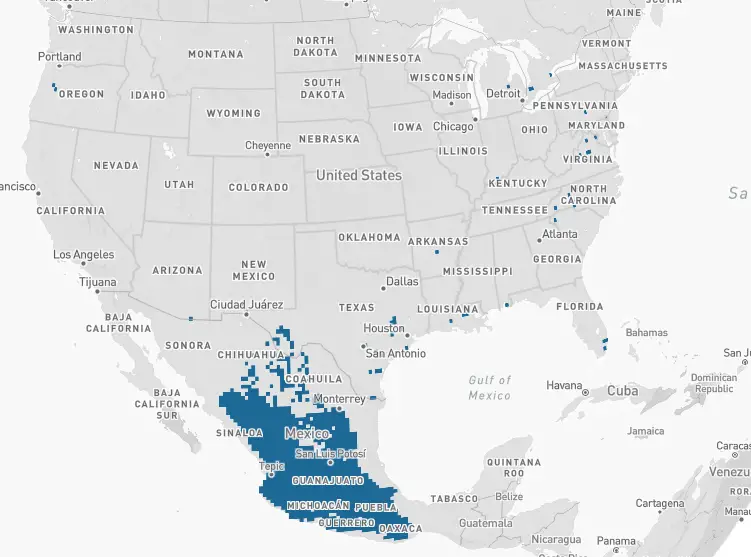
Arkansas Allen’s, Black-chinned, Broad-billed, Broad-tailed, Buff-bellied, Calliope, Mexican violetear, Rivoli’s, and Rufous hummingbirds travel south to over-winter in Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Anna’s over-winter in upper Mexico and California.
Ruby-throated over-winter in Arkansas.
Allen’s – The Allen’s hummingbird overwinters primarily in Southern California. The Allen’s hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including Texas, Tennessee, and as far north as Maryland, New York, and Wisconsin.
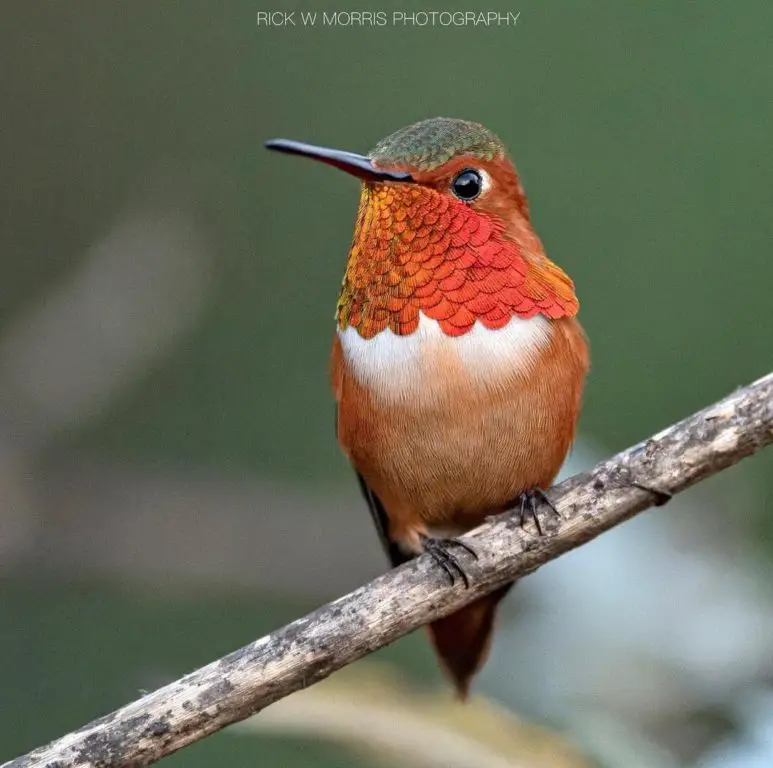

Photo by: IntheWildwithRick
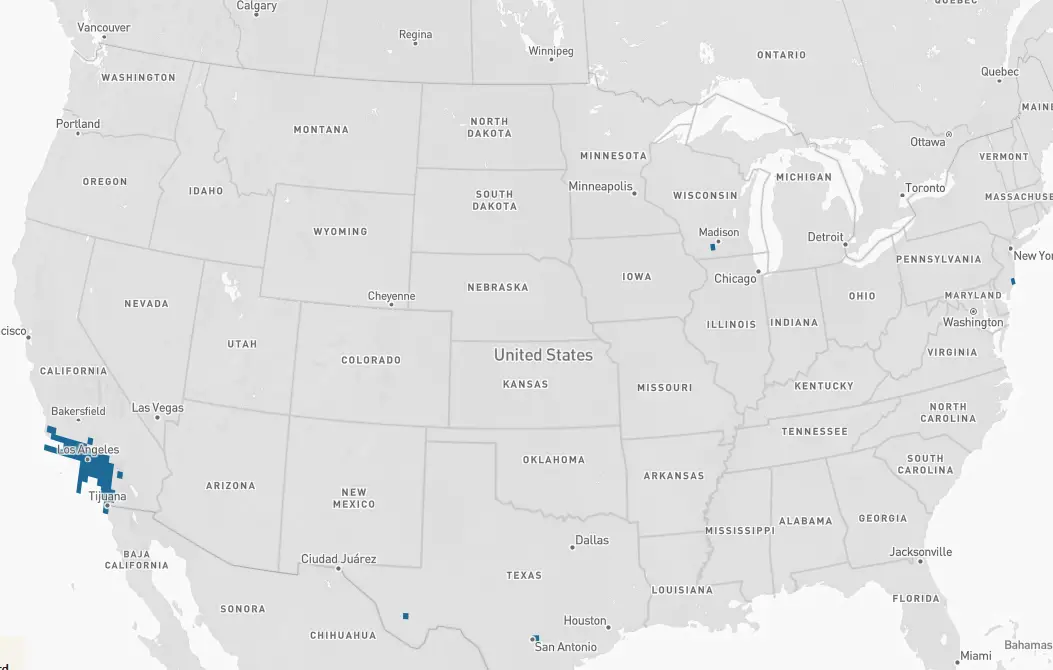
Black-chinned – The Black-chinned hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico. Black-chinned hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Florida, Georgia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and as far north as Maryland and Pennsylvania.
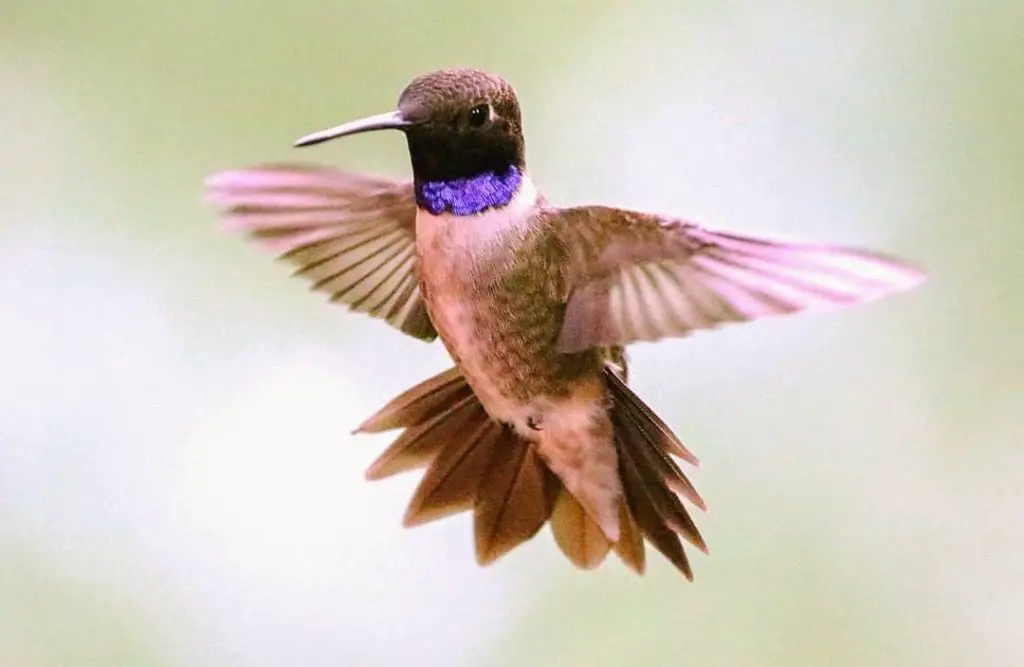

Photo by: bird.whisperer
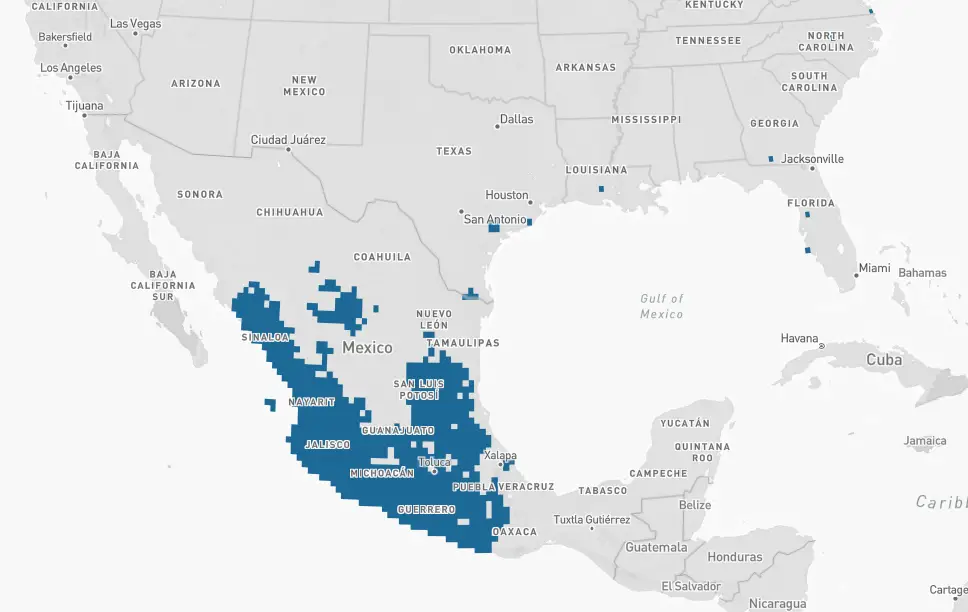
Broad-billed – The Broad-billed hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico. Broad-billed hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including Texas, Arizona, Louisiana, Florida, and Utah.
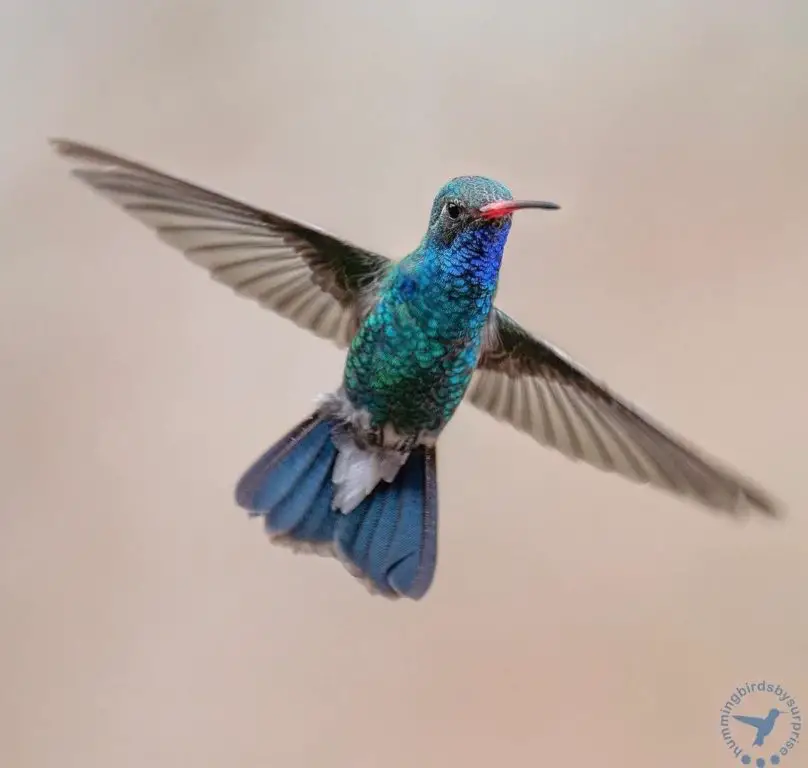

Photo by: hummingbirdsbysuprise
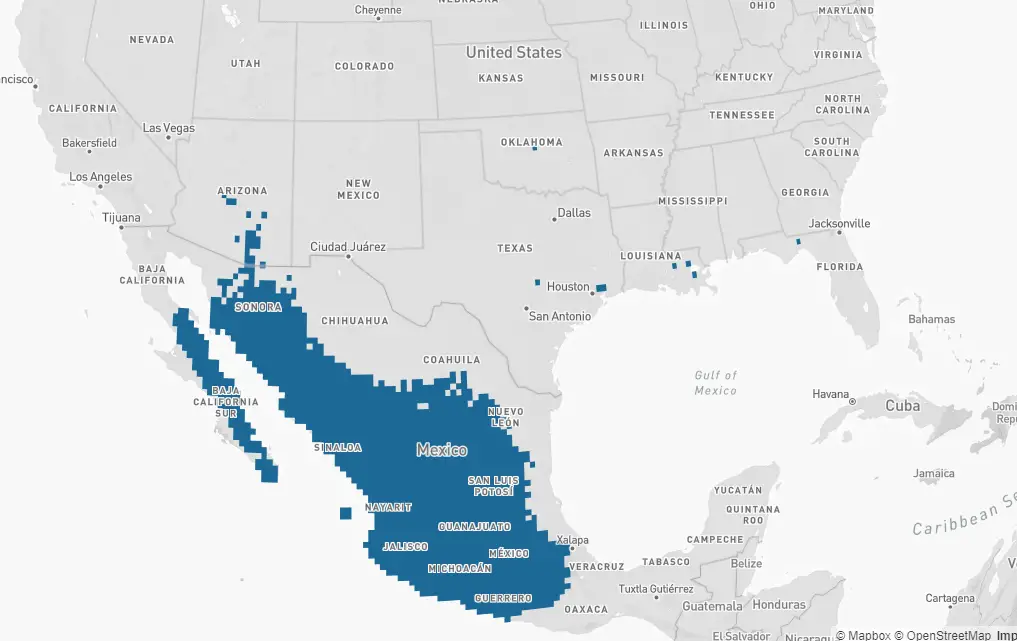
Broad-tailed – The Broad-tailed hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico and Guatemala. Broad-tailed hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas in Western Texas.
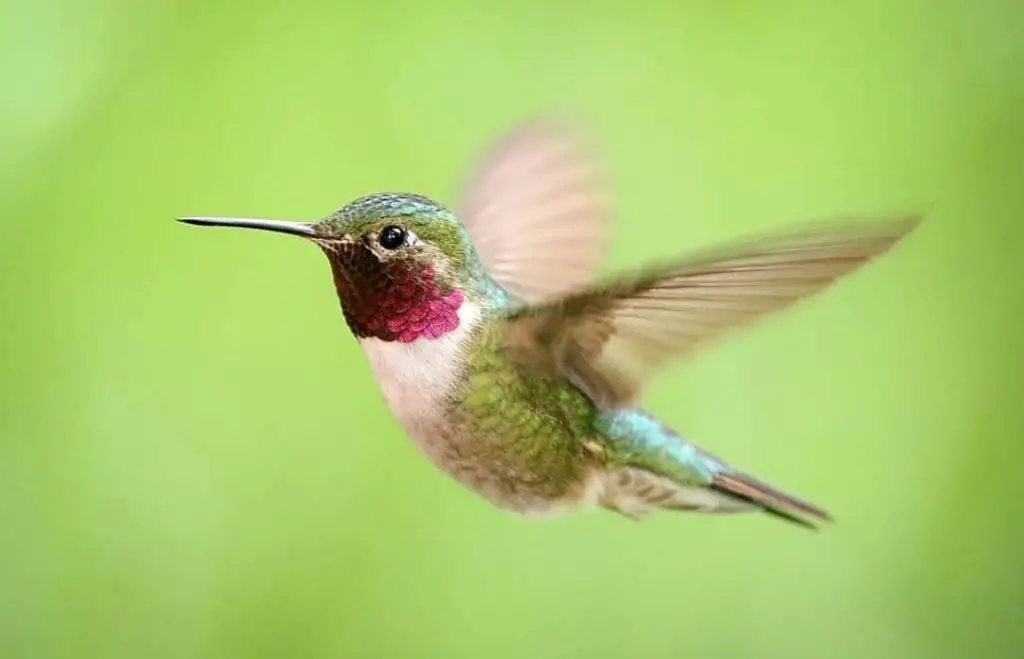

Photo by: bird.whisperer
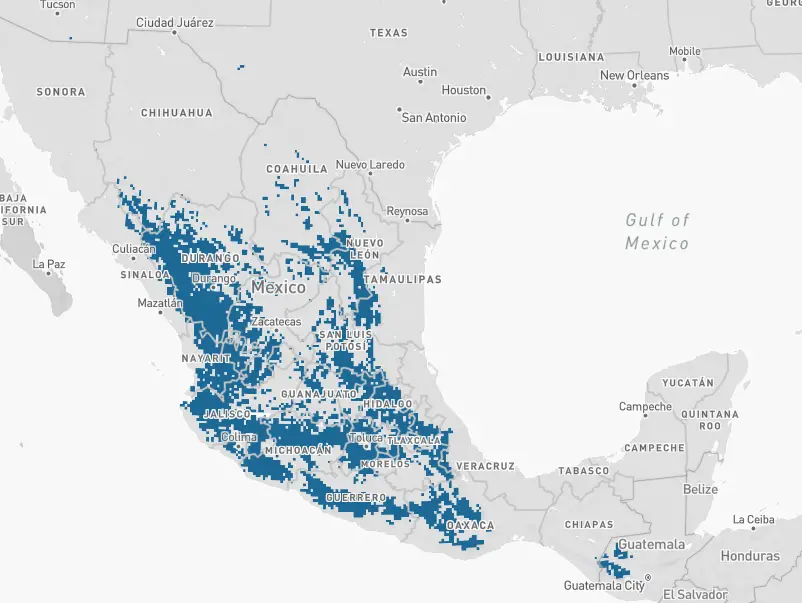
Buff-bellied – The Buff-bellied hummingbirds are not really migratory and live year-round in Southern Texas and the Gulf Coast of Mexico.
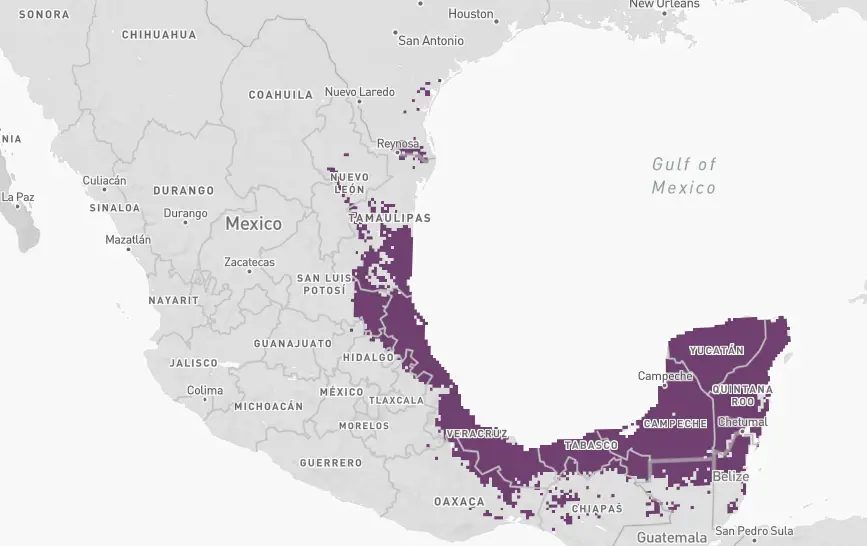
Calliope – The Calliope hummingbird overwinters primarily on the west coast of Mexico. Calliope hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York.
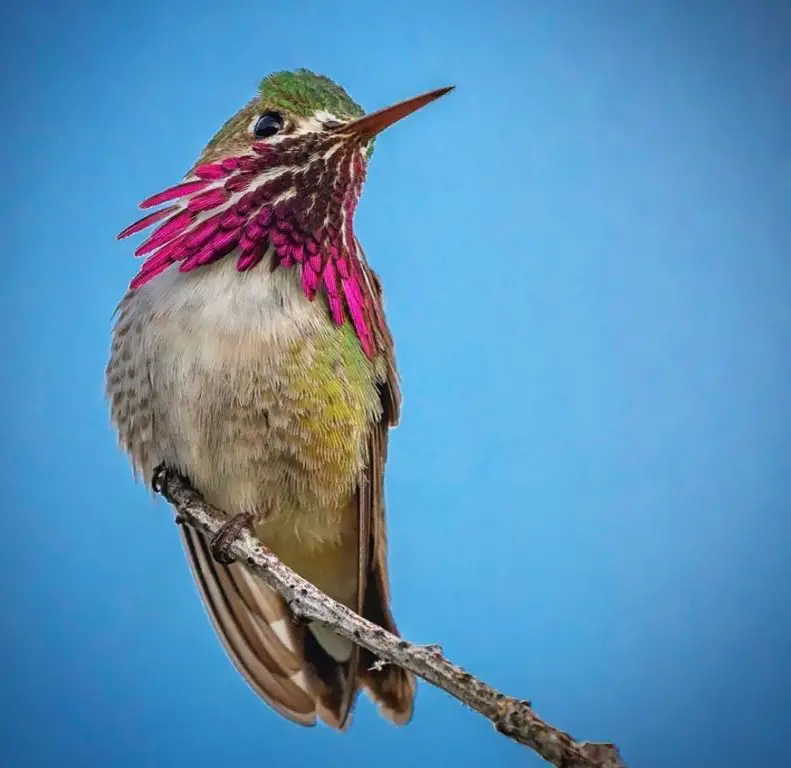

Photo by: sony_alpha_male
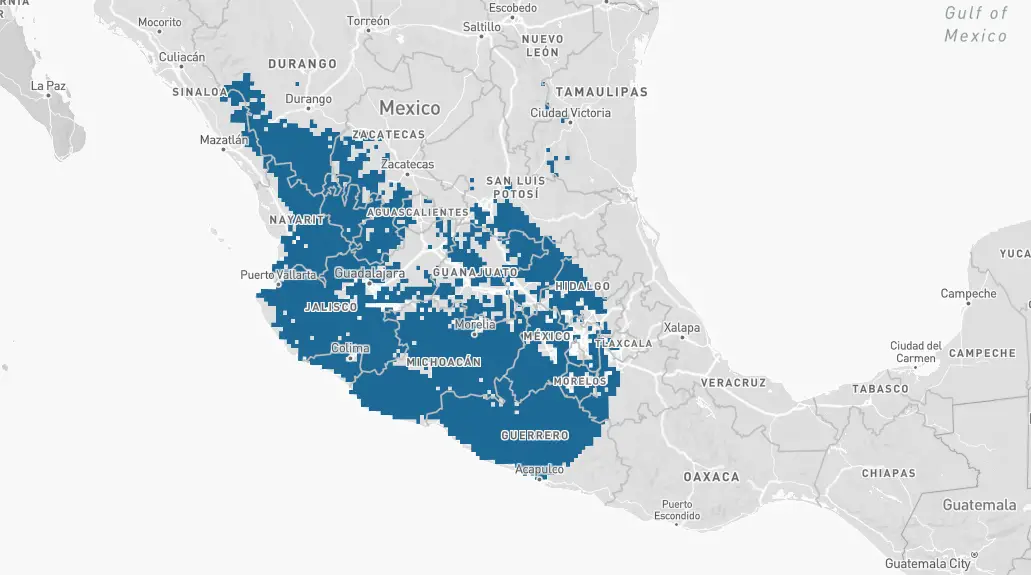
Mexican Violetear – The Mexican Violetear hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras. Mexican Violetear hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including Arizona, Texas, and Louisiana.
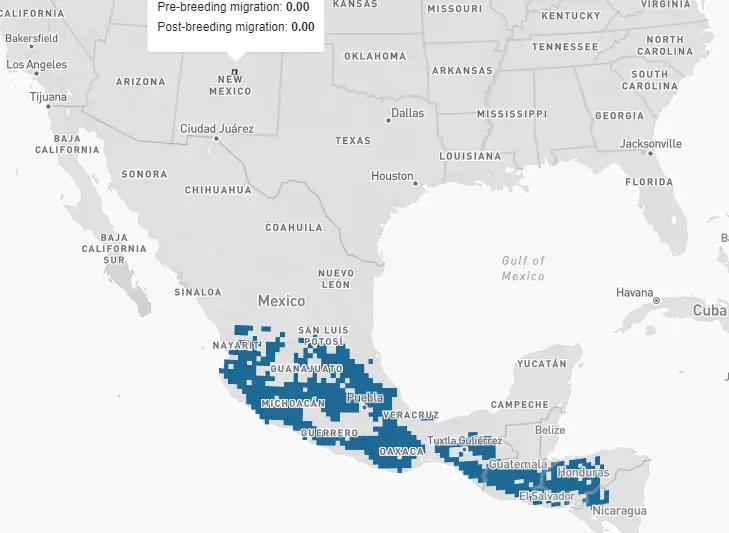
Rivoli’s – The Rivoli’s hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua. Some Ravioli’s hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas of Southern Arizona and Western Texas.
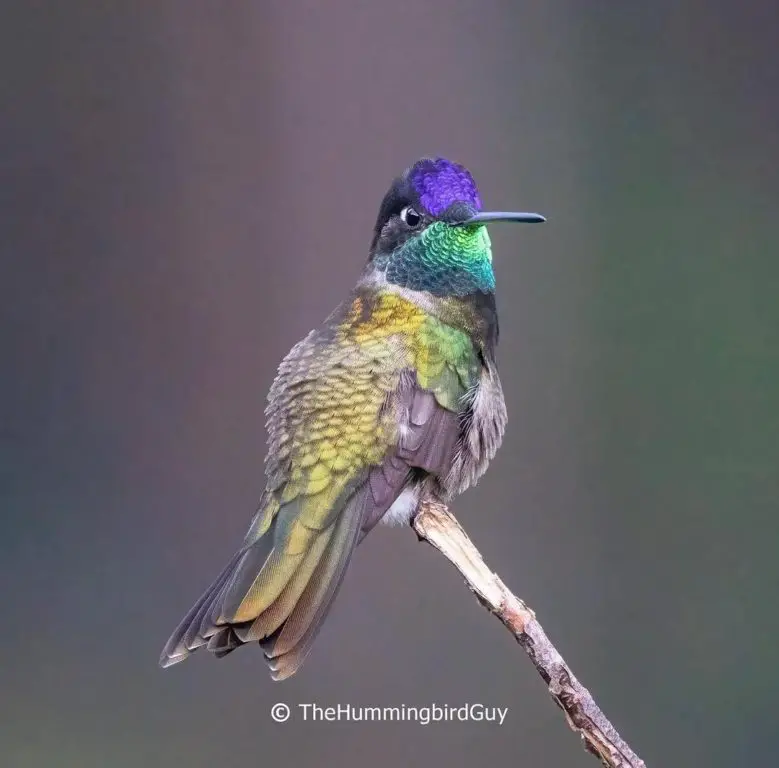

Photo by: thehummingbirdguy
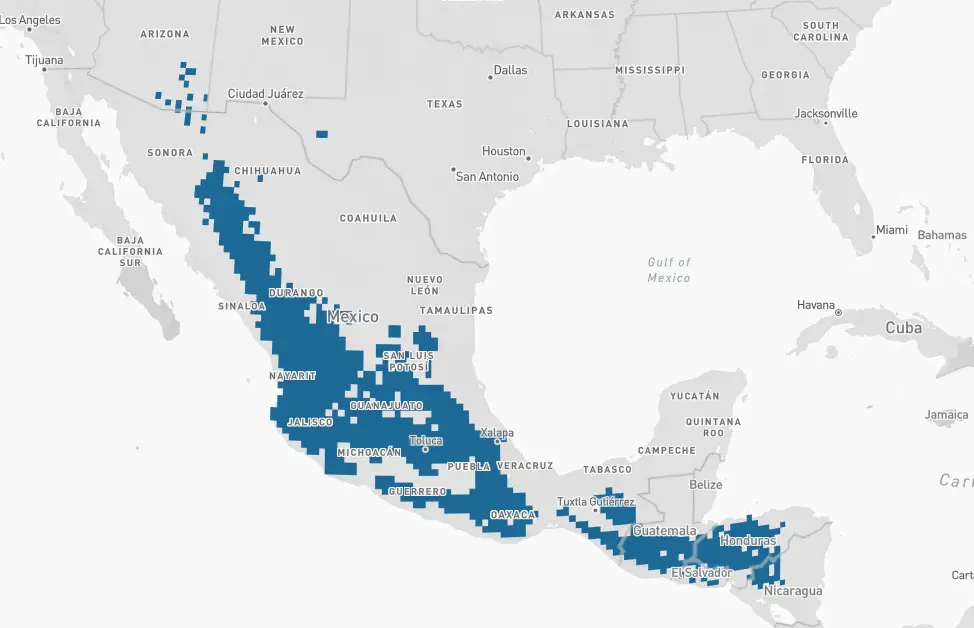
Anna’s – The Anna’s hummingbird overwinters primarily in Southern California and the upper parts of Baja and Mexico. Anna’s hummingbirds are seen in some years, during winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including Texas, Missouri, Illinois (Chicago area), Maryland, Utah, and Idaho.

Photo by: Kevin Walsh
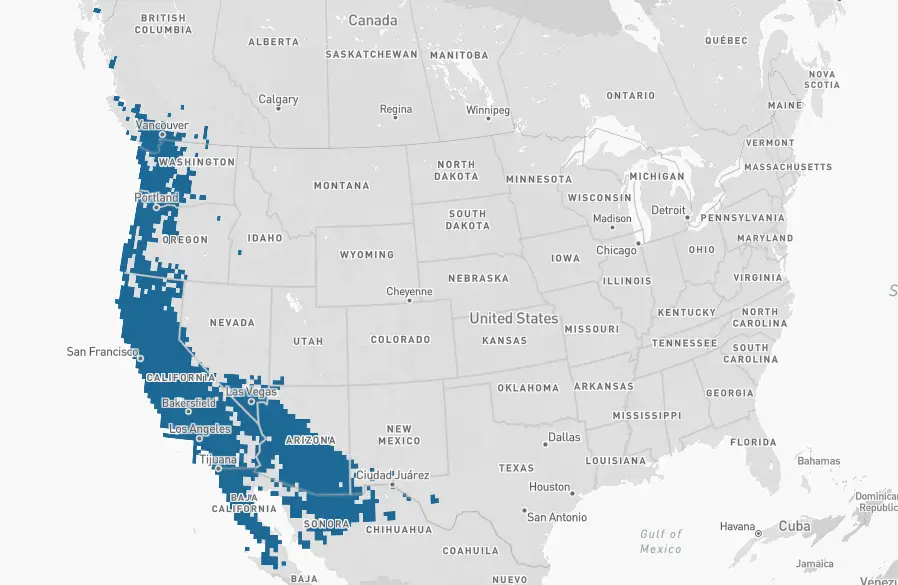
Rufous – The Rufous hummingbird overwinters primarily in Mexico. Rufous hummingbirds are seen in some years, during the winter months, in scattered areas throughout the USA including New Mexico, Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Georgia, Florida, Tennessee, North and South Carolina, Virginia, Kentucky, Missouri, Illinois, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Vermont, Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota.

Photo by: Kevin Walsh
Every hummingbird has an exceptional memory. Throughout their spring migration, they can recall every flower or feeder they visited, and they will revisit those spots every year.
Hummingbirds have been seen to return to a feeder even after it has been removed for a few years.
See my article: Hummingbird Adaptation and Remarkable Ability to Locate Food
Check out my other posts on Hummingbird Questions
Happy Hummingbird Watching!
Backyard Visitors is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. We also participate in other affiliate programs which compensate us for referring traffic.
